The credit score is calculated based on various factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit, and recent credit inquiries. Having a good credit score is important as it can determine your eligibility for loans, credit cards, and other financial transactions.
A higher credit score indicates a lower risk for lenders, making it easier for you to secure favorable borrowing terms. Understanding how your credit score is calculated can help you identify areas for improvement and take steps to maintain or improve your score.
By taking proactive measures to manage your credit responsibly, you can enhance your financial stability and achieve your financial goals.

Factors Affecting Credit Score
How is Credit Score Calculated influenced by several factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit used, and new credit inquiries. These elements play a significant role in determining an individual’s creditworthiness.
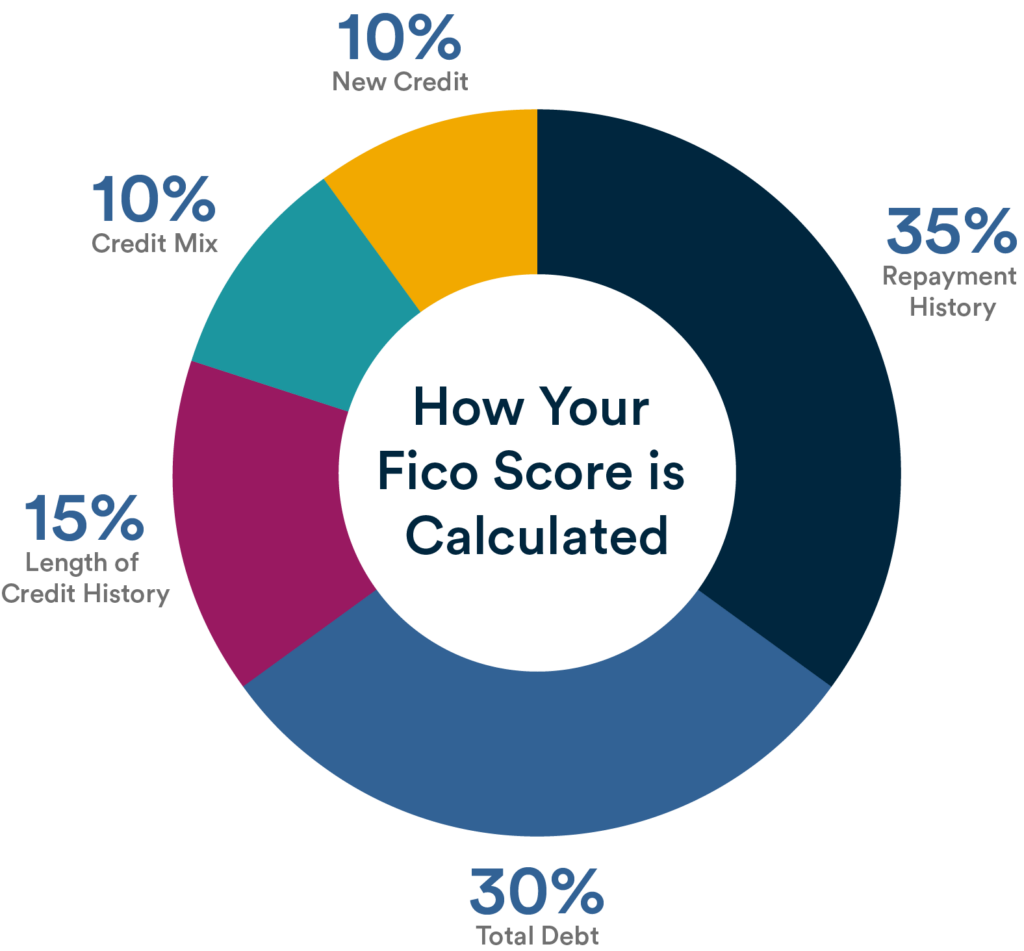
When it comes to understanding your credit score, it’s important to know the factors that affect it. Your credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, and it is used by lenders to determine your eligibility for loans, credit cards, and other financial products. Several factors are taken into consideration when calculating your credit score, including payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, credit mix, and new credit inquiries.
Payment History
Your payment history is one of the most influential factors when it comes to determining your credit score. It reflects how responsible you have been in making your payments on time. Lenders want to see a consistent record of on-time payments, as it demonstrates your ability to manage your debts effectively. Late payments, missed payments, or defaulting on loans can significantly lower your credit score. It’s crucial to prioritize making your payments on or before their due dates to maintain a positive payment history.
Credit Utilization
Credit utilization refers to the amount of available credit you are currently using. It is calculated by dividing your outstanding credit card balances by your total credit limit. Lenders consider credit utilization because it indicates how reliant you are on credit. Ideally, you should aim to keep your credit utilization below 30% of your available credit limit. Keeping your credit utilization low shows lenders that you can responsibly manage your credit and not be overly reliant on it.
Length Of Credit History
How is Credit Score Calculated history plays a role in determining your credit score. Lenders prefer borrowers with a longer credit history as it provides them with more information about your borrowing habits and repayment patterns. If you are just starting to build your credit, it’s important to establish a good track record from the beginning. Lenders like to see a proven history of responsible borrowing and repayment over time.
Credit Mix
Having a diverse credit mix can positively impact your credit score. This means having a healthy combination of different types of credit, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages. Lenders want to see that you can manage different types of credit responsibly. However, it’s important to note that it’s not necessary to take on debt just to improve your credit mix. Only take on credit that you actually need and can manage effectively.
New Credit Inquiries
When you apply for new credit, such as a loan or credit card, it generates what is known as a hard inquiry on your credit report. Multiple hard inquiries within a short period of time can have a negative impact on your credit score. Lenders may perceive multiple credit inquiries as a sign of financial instability or desperation for credit. On the other hand, soft inquiries, which occur when you check your credit report or when creditors pre-approve you for an offer, do not affect your credit score.
Optimizing these factors is crucial for improving your credit score and maintaining good credit health. By focusing on your payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, credit mix, and new credit inquiries, you can take control of your financial well-being and work towards achieving a strong and favorable credit score.
Credit: www.laurelroad.com
Payment History
One of the key factors that influence your credit score is your payment history. Lenders and credit bureaus analyze your payment behavior to assess how reliable you are in repaying your debts. A positive payment history is crucial for maintaining a good credit score, while late payments, missed payments, or significant financial setbacks like bankruptcies or foreclosures can have a negative impact on your creditworthiness.
On-time Payments
When you consistently make on-time payments, you demonstrate financial responsibility and a willingness to fulfill your obligations. Lenders view this as a positive sign and may be more likely to approve credit applications or offer favorable terms. On-time payments not only boost your credit score, but they also contribute to a positive payment history that can strengthen your overall creditworthiness.
Late Payments
Unfortunately, life can throw unexpected challenges that may cause you to make late payments. A late payment occurs when you fail to submit your payment by the due date agreed upon with the creditor. While a single late payment might not have a significant impact on your credit score, consistently making late payments can be detrimental. Lenders and credit bureaus consider late payments as a reflection of financial instability and may view you as a higher credit risk.
Missed Payments
Missing a payment altogether can have severe consequences for your credit score. It occurs when you fail to make a payment before the due date or within the grace period provided by the lender. Missed payments are a red flag to creditors and can lead to negative credit reporting. Additionally, missed payments can result in penalty fees and increased interest rates, making it even more challenging to catch up on your outstanding debts.
Bankruptcies Or Foreclosures
In unfortunate circumstances, individuals may undergo bankruptcies or face foreclosure due to overwhelming financial difficulties. These events have a significant impact on your credit score and can stay on your credit report for several years. Bankruptcies signal a severe inability to repay debts, and lenders may view you as a high-risk borrower. Similarly, foreclosures indicate defaulting on a mortgage loan, further damaging your creditworthiness.
In conclusion, a positive payment history, consisting of on-time payments and an absence of late or missed payments, is vital in maintaining a good credit score. Bankruptcies or foreclosures, on the other hand, have a major negative impact on creditworthiness. Being aware of how your payment history affects your credit score can help you make informed financial decisions and maintain a healthy credit profile.
Credit Utilization
Credit utilization is a significant factor in determining your credit score. It measures how much of your available credit you are currently using. A high credit utilization ratio can negatively impact your credit score, while a lower ratio can help improve it. Let’s dive into the various aspects of credit utilization that affect your credit score:
The balance-to-limit ratio, also known as the credit utilization ratio, calculates the percentage of your available credit that you have utilized. It is calculated by dividing your total credit card balances by your total credit limits. The lower your balance-to-limit ratio, the better it is for your credit score.
| Credit Card Balances: | Credit Limits: | Balance-to-Limit Ratio: |
|---|---|---|
| $500 | $2,000 | 25% |
| $1,000 | $2,000 | 50% |
As you can see in the table above, a lower balance-to-limit ratio demonstrates responsible credit usage and can positively impact your credit score. Therefore, it’s important to keep your credit card balances as low as possible in relation to your credit limits.
The number of credit accounts you have also contributes to your credit utilization. Lenders and credit bureaus consider the number of open accounts you have, including credit cards, loans, retail accounts, and mortgages. Having a good mix of credit accounts, such as a mix of credit cards and installment loans, can positively impact your credit score.
Individual credit card balances are another aspect of credit utilization. Higher balances on individual credit cards indicate a higher credit utilization ratio and can negatively impact your credit score. It’s advisable to keep your credit card balances low and manageable, aiming to pay off the full balance each month.
In conclusion, maintaining a low balance-to-limit ratio, having a good number of credit accounts, and keeping credit card balances in check are crucial factors in determining your credit utilization and, consequently, your credit score. By managing these aspects wisely, you can improve your creditworthiness and increase the chances of accessing favorable credit options in the future.
Length Of Credit History
In the world of credit scoring, your credit history plays a crucial role in determining your creditworthiness. One of the key factors that lenders consider when assessing your creditworthiness is the length of your credit history. In other words, how long you have been using credit and managing your debts. This factor is broken down into three important subcategories:
1. Age Of Oldest Account
The age of your oldest account is an essential piece of information that contributes to your credit score. Lenders look at the age of your oldest account because it indicates your experience in managing credit over an extended period. A long-standing account demonstrates your ability to handle credit responsibly and gives lenders more confidence in your financial reliability.
2. Average Age Of Accounts
Not only does the age of your oldest account matter, but the average age of all your accounts is also considered. The idea here is to evaluate the overall depth of your credit history. Lenders will take into account the duration of each individual account and then calculate the average age across all of your accounts. A higher average age shows a longer credit record, indicating to lenders that you have a more established financial history.
3. Recent Account Activity
While the age of your oldest account and the average age of your accounts are important, your recent account activity also plays a role in determining your credit score. Lenders consider how recently you have opened new accounts, applied for credit, or made any other significant changes to your credit profile. An excessive amount of recent activity might raise concerns about your financial stability, as it could be an indication of a higher risk of defaulting on your debts.
As you can see, the length of your credit history is a significant factor that influences your credit score. It is essential to maintain a healthy credit history by having a well-established oldest account, a good average age of all your accounts, and avoiding too much recent account activity.
Credit Mix
How is Credit Score Calculated mix is one of the factors that contribute to calculating your credit score. It refers to the different types of credit you have, such as loans and credit cards. Having a diverse credit mix can positively influence your credit score.
Types Of Credit Accounts
In order to understand how your credit score is calculated, it’s important to consider the types of credit accounts you have. Your credit mix plays a significant role in determining your creditworthiness and overall financial health.
There are several different types of credit accounts that lenders take into account when evaluating your credit score:
- Credit cards
- Loans
- Mortgages or auto loans
Credit Cards Vs. Loans
When it comes to building a positive credit history, understanding the differences between credit cards and loans is crucial. Both of these types of credit accounts impact your credit score, but in different ways.
Credit cards are revolving accounts that allow you to make purchases up to a certain credit limit. The balances on your credit cards are reported to credit bureaus, and it’s important to keep your credit utilization ratio low by paying off your balances in full and on time.
Loans, on the other hand, are installment accounts that involve borrowing a specific amount of money and repaying it over a set period of time. Examples of loans include personal loans, student loans, and auto loans. Making regular, on-time payments towards your loan can boost your credit score.
Mortgages Or Auto Loans
Lastly, mortgages and auto loans are considered secured loans because they are backed by collateral (your home or car). These loans have a significant impact on your credit score, as lenders view them as long-term financial commitments.
It’s important to make timely payments on your mortgage or auto loan to demonstrate responsible financial management and maintain a healthy credit score. Missing payments or defaulting on these loans can have a detrimental effect on your creditworthiness.
Overall, having a diverse credit mix that includes different types of credit accounts can demonstrate your ability to manage various financial responsibilities. By maintaining a mix of credit cards, loans, and secured loans, you can work towards achieving a higher credit score and improving your overall financial profile.
New Credit Inquiries
Credit scores are calculated using various factors. One important component is the number of new credit inquiries you have. These inquiries can impact your score, so it’s wise to be mindful of applying for new credit too frequently.
When it comes to calculating your credit score, new credit inquiries play a significant role. These inquiries occur when you apply for new credit, whether it’s a credit card, a car loan, or a mortgage. Lenders use this information to assess the level of risk involved in lending you money.
Number Of Recent Credit Applications
The number of recent credit applications you have can impact your credit score. Each time you apply for credit, whether you’re approved or not, it leaves a mark on your credit history. Having too many credit applications within a short period of time can raise concerns for lenders, as it may indicate financial instability or overextending your credit.
To maintain a healthy credit score, it’s important to be mindful of the number of credit applications you make. Avoid applying for multiple credit cards or loans within a short timeframe, as this can negatively impact your credit score. Instead, focus on applying for credit only when necessary and ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria before submitting an application.
Credit Checks By Lenders
When you apply for new credit, lenders will typically conduct a credit check to evaluate your creditworthiness. These credit checks can be classified as either “hard inquiries” or “soft inquiries.”
A hard inquiry occurs when you apply for credit and authorize the lender to review your credit report. Hard inquiries can have a slight negative impact on your credit score, as they suggest that you are actively seeking credit.
On the other hand, soft inquiries occur when a person or company checks your credit as part of a routine review or pre-approval process. Soft inquiries do not affect your credit score and are usually performed without your consent. These include credit checks by insurance companies, potential employers, or even when you check your own credit score.
It’s important to note that while hard inquiries may have a small impact on your credit score, the effect is typically temporary. Multiple hard inquiries within a short timeframe, such as when you’re shopping for a mortgage or auto loan, are usually treated as a single inquiry and have minimal impact on your score.

FAQ Of How Is Credit Score Calculated
How Is Credit Score Calculated?
Credit score is calculated based on several factors including your payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit used, and new credit inquiries. Each factor carries a different weight in the calculation, and the three major credit bureaus use mathematical algorithms to determine your score. Regularly checking your credit report and making timely payments can help improve your credit score over time.
What Is A Good Credit Score?
A good credit score typically falls within the range of 670 to 850. A higher score indicates that you have a lower risk of defaulting on credit obligations. Lenders consider a good credit score as a positive signal for lending. However, credit score requirements may vary depending on the lender and the type of credit you are applying for.
Can You Improve Your Credit Score?
Yes, you can improve your credit score. Start by paying your bills on time, as payment history is a crucial factor in your score. Additionally, reducing your credit card balances and limiting new credit inquiries can positively impact your score. Regularly monitoring your credit report can help you identify any errors or discrepancies that may be affecting your score.
How Long Does It Take To Improve A Credit Score?
The time it takes to improve your credit score depends on several factors, including the current state of your credit and your actions to improve it. Generally, significant improvements can be seen within six months to a year with consistent efforts to make on-time payments, reduce debt, and practice healthy credit habits. However, it is essential to note that credit repair is a gradual process and may vary for each individual.
Conclusion
Understanding how credit scores are calculated is essential for anyone seeking to improve their financial standing. By considering factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, new credit applications, and credit mix, individuals can make informed decisions that positively impact their credit scores.
Keeping track of these elements and maintaining responsible credit habits are key to ensuring a strong credit score and financial well-being. So, start taking control of your credit today and work towards a brighter financial future.
