Credit scores started in 1989 with the introduction of FICO scores. Prior to that, creditworthiness was determined through subjective evaluations by lenders. “When Did Credit Scores Start”
The use of credit scores revolutionized the lending industry by providing a standardized and objective way to assess an individual’s credit risk. Today, credit scores play a crucial role in determining interest rates, loan approvals, and even job applications. They are based on factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit, and new credit inquiries.
Understanding the history and significance of credit scores is essential for anyone looking to improve their financial health and access better borrowing opportunities.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/credit-score-factors-4230170-v22-897d0814646e4fc188473be527ea7b8a.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Early Credit Assessment
In 1956, the use of credit scoring began to take hold. The history of credit scores dates back to the late 1950s and early 1960s, with the first complete credit scoring system being implemented in 1958. This new method revolutionized the lending and credit industry, providing a more standardized and objective measure for assessing creditworthiness.
Origins Of Credit Assessment
In the world of finance, credit assessment plays a vital role in determining an individual’s creditworthiness. But have you ever wondered when this practice of assessing credit started? Well, let’s take a journey through time and explore the early origins of credit assessment.
Pre-credit Score Methods
Before the advent of credit scores, lenders used various methods to assess an individual’s creditworthiness. These methods relied on a combination of personal judgment, character references, and financial information. Let’s take a look at some of the pre-credit score methods that were employed in the early days of credit assessment:
- Character References: Lenders would rely on the opinions of trusted individuals who could vouch for the borrower’s reputation and reliability. These references would provide insights into the borrower’s character and integrity.
- Financial Statements: Borrowers would be required to submit detailed financial statements, including income, expenses, and assets. Lenders would analyze these statements to assess the borrower’s ability to repay the debt.
- Credit References: Lenders would contact other lenders or suppliers with whom the borrower had previous financial interactions. These references would provide information about the borrower’s payment history and creditworthiness.
- Collateral: In certain cases, lenders would require borrowers to provide collateral against the loan. This collateral would serve as a form of security for the lender in case the borrower defaulted on the loan.
While these methods provided some form of credit assessment, they were subjective and prone to biases. Lenders often had to rely on their own judgment and intuition to make lending decisions. This lack of standardized assessment led to inconsistencies and inefficiencies in the credit industry.
Fortunately, the credit assessment landscape underwent a significant transformation with the introduction of credit scores. These scores provided a standardized and objective measure of an individual’s creditworthiness, making the lending process more efficient and transparent.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-credit-score-car-dealers-really-use-3974683_final-84652120491b4ed6a279f7217213fec8.png)
Credit: www.thebalancemoney.com
Introduction Of Credit Scores
Credit scores were introduced in 1989, marking a significant turning point in the history of credit. Prior to that, creditworthiness was determined through other means. Today, credit scores play a crucial role in determining an individual’s financial health and eligibility for loans and other forms of credit.
Transition To Numeric Evaluation
Before the introduction of credit scores, lenders relied on subjective evaluation methods to determine an individual’s creditworthiness. They would review an applicant’s financial information, employment history, and references to make a judgment call. However, this process lacked consistency and was often prone to bias.
In 1956, the concept of credit scoring took hold, marking a significant transition in the evaluation of creditworthiness. Lenders started using statistical models to assess the credit risk associated with a borrower. These models assigned a numeric value to different factors, such as payment history, debt levels, and length of credit history, to calculate a credit score.
Emergence Of Major Credit Bureaus
The advent of credit scores was accompanied by the rise of major credit bureaus. These bureaus collected and maintained vast databases of individuals’ credit information, becoming the primary source for credit reports and scores.
Equifax, one of the three major credit bureaus, was established in 1899 and initially focused on providing services to the retail industry. Experian, another leading credit bureau, traces its origins back to 1826 when it began as a business and financial information provider. TransUnion, the third major credit bureau, was founded in 1968 as a holding company for a railcar leasing business and later expanded into credit services.
Together, these credit bureaus played a pivotal role in the development and expansion of credit scores. They collected and analyzed vast amounts of credit data from lenders and other sources, allowing for a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of creditworthiness.
Evolution Of Scoring Models
Credit Scores have become an integral part of the modern financial system, shaping the way banks and financial institutions evaluate and offer credit to individuals and businesses. The evolution of scoring models has played a pivotal role in making credit scores accessible and reliable and has significantly impacted the financial landscape. Here, we’ll explore the Evolution of Scoring Models and dive into the development of FICO scores and the expansion of credit scoring models.
Development Of Fico Score
One of the most significant milestones in the evolution of credit scoring models was the development of the FICO score. Introduced in the late 1980s, the FICO score revolutionized the assessment of creditworthiness by using a proprietary algorithm to evaluate an individual’s credit history and provide a numerical representation of their credit risk. “When Did Credit Scores Start”
Expansion Of Credit Scoring Models
Over the years, credit scoring models have expanded to encompass a broader range of financial data and factors, leading to the development of alternative credit scoring models. These models take into account non-traditional data, such as utility payments, rental history, and other non-credit-based information, to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s creditworthiness.
Impact On Financial Landscape
When credit scores were introduced in 1989, they revolutionized the financial landscape, playing a crucial role in lending decisions and influencing consumer behavior. Credit scores provided lenders with a standardized method to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers, enabling them to make more informed decisions.
Role In Lending Decisions
Credit scores have become an integral part of the lending process, with lenders relying heavily on them to determine the creditworthiness of borrowers. These scores serve as a quick snapshot of an individual’s credit history, providing lenders with a measure of their risk potential.
Key points:
- Credit scores help lenders assess the likelihood of timely loan repayments.
- Lenders often set minimum credit score requirements for loan approval.
- Higher credit scores may result in more favorable loan terms and lower interest rates.
- Lower credit scores may lead to loan denials or less favorable loan terms.
Influence On Consumer Behavior
Credit scores have not only impacted lending decisions but have also had a profound influence on consumer behavior. Individuals are now more aware of the importance of maintaining a good credit score and how it can affect their financial well-being. As a result, people have become more conscious of their credit habits and repayment behavior.
Key points:
- Consumers strive to improve their credit scores to qualify for better loan terms and opportunities.
- A high credit score can open doors to lower interest rates for mortgages, auto loans, and credit cards.
- People with lower credit scores may face challenges in accessing credit and may need to settle for less favorable terms.
- The awareness of credit scores has led to an increase in financial education and responsible borrowing.
In conclusion, credit scores have had a significant impact on the financial landscape, affecting both lending decisions and consumer behavior. They have provided lenders with a standardized assessment tool and encouraged individuals to become more responsible with their credit habits. Understanding how credit scores function is crucial for individuals looking to navigate the world of finance effectively.
Future Of Credit Scores
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the future of credit scores holds great potential for transformation. From technological advancements to potential reforms, the landscape of credit scoring is poised to become increasingly sophisticated and tailored to individual needs.
Technological Advancements
With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics, credit scoring algorithms are becoming more accurate and efficient. These technologies enable lenders to assess creditworthiness in real-time, taking into account a broader range of factors beyond traditional credit history.
AI-powered algorithms can analyze alternative data sources such as utility bill payments, rental history, and even social media activity, creating a more comprehensive picture of an individual’s financial behavior. This means individuals with little to no credit history can still be evaluated fairly based on their financial habits.
Potential Reforms
The future of credit scores also entails potential reforms to address existing limitations and disparities. One such reform is the inclusion of rent payments in credit reports. Since a significant portion of the population pays rent rather than a mortgage, this change would provide a fairer representation of an individual’s financial responsibility.
Another potential reform is the implementation of a universal credit score system. Currently, different lenders use various credit scoring models, leading to discrepancies between scores. A universal score system would standardize credit evaluations, allowing individuals to have a clearer understanding of their creditworthiness.
Furthermore, efforts are being made to reduce the impact of negative information on credit scores. Some reforms propose shorter reporting periods for certain negative events, such as medical debt or late payments. These changes aim to prevent individuals from being unduly penalized for temporary setbacks that may not accurately reflect their overall creditworthiness.
In conclusion, the future of credit scores is a promising one, characterized by technological advancements and potential reforms. Through the utilization of AI and big data analytics, credit scoring algorithms are becoming more accurate while also considering alternative data sources. Additionally, potential reforms such as the inclusion of rent payments and the implementation of universal credit scoring systems aim to create a fairer and more transparent credit evaluation process.
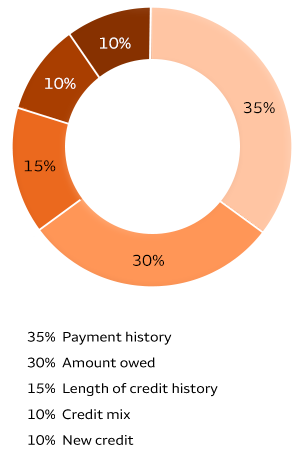
Credit: www.wellsfargo.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of When Did Credit Scores Start
Did Credit Scores Exist Before 1989?
Credit scores did not exist before 1989. The notion of credit scoring first emerged in the 1950s, but it wasn’t until 1989 that the FICO score system was established, transforming the credit business
When Did They Start Using A Credit Score?
Credit scores were first introduced in 1989. Initially, they were employed to determine creditworthiness.
Is It Possible To Have A Credit Score Of 900?
No, it is not possible to have a credit score of 900. The highest credit score range is typically 850.
What Is Everyone’s First Credit Score?
There isn’t a set credit score that everyone starts with. If you have no credit history, you likely don’t have a score at all.
Conclusion
The history of credit scores dates back to 1956 and has steadily evolved since then. There isn’t a specific starting credit score for individuals, but credit scoring has had a significant impact on financial systems. Understanding the origins and implications of credit scores is crucial for financial literacy.
